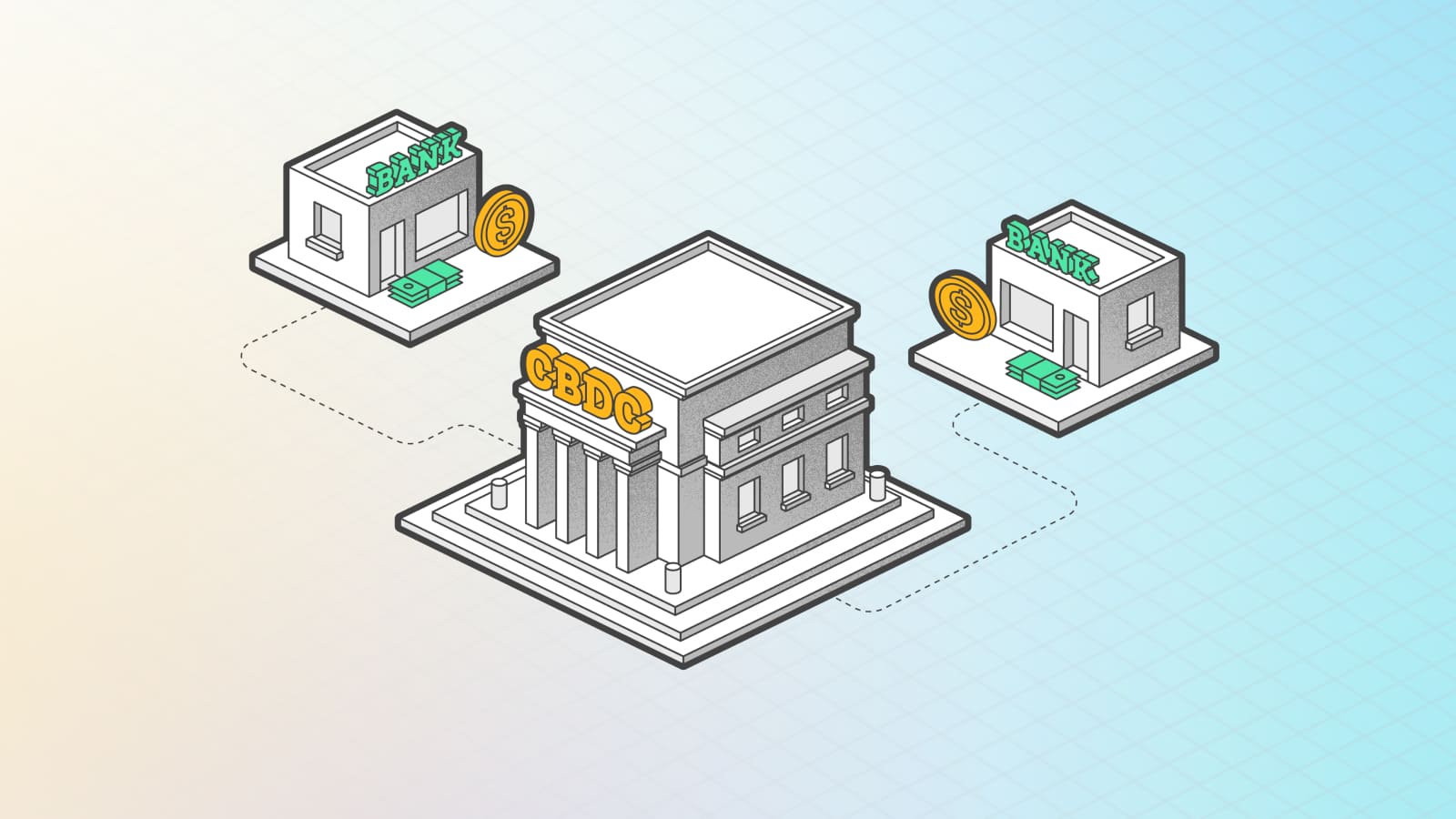
CBDC is a central bank digital currency, the equivalent of fiat money. Although CBDC is used in a limited number of countries (a full-fledged launch took place only in 11 countries), the introduction of CBDC is being considered or planned worldwide. For example, 19 of the 20 G20 countries are in the development stage of a state digital currency, and nine have launched a pilot version.
In the article, we will tell you what CBDC is, how it differs from fiat and cryptocurrencies, how the issue occurs, and how experts estimate its prospects.
CBDC: Definition and Basic Concept
CBDC (central bank digital currency) is pegged to the state fiat currency at a ratio of 1:1. Although the concept of digital currency is similar to cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, CBDC has features such as state control, centralization, and stability. In terms of functionality, CBDC is a digital version of fiat money.
The concept of a state-controlled digital currency has been around for a long time. One of the first prototype systems was launched in 2014 in Ecuador — at the peak of development, it had more than 500,000 users with deposits totaling over $10 million. The system existed until 2018.
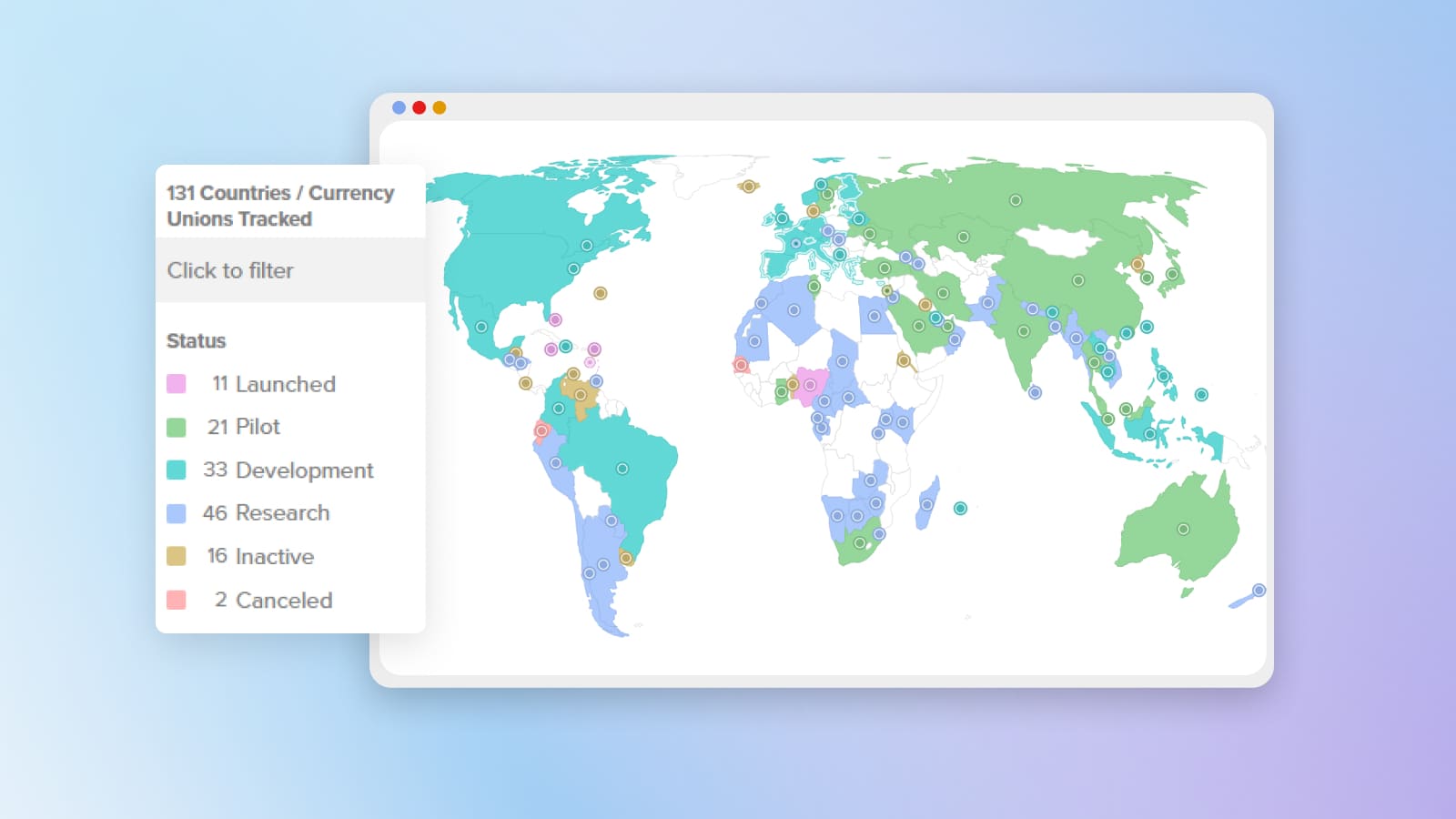
Also in 2014, China announced the development of a digital yuan. The project was launched in 2021. This is how the first digital currency accepted in the global economy appeared. Other successful examples of state digital currencies include Nigeria (eNaira), Bahamas (Sand Dollar), Jamaica (Jam-Dex). Several countries are in the CBDC development stage. Among them are the US, UK, France, Sweden, New Zealand and others.
CBDC, Fiat and Cryptocurrency: Main Differences
Although CBDC, like cryptocurrencies, is a digital currency, it has several important distinguishing points from cryptocurrencies and stablecoins:
- Centralization. The issuer of a centralized digital currency is a public authority.
- State control. The central bank has access to the electronic wallets of CBDC users. Production, distribution, use of digital currency is controlled by government agencies or financial organizations.
- Restrictions on cross-border payments. If cryptocurrency can be transferred to a user from anywhere in the world, the state currency can be used only within the country or in accordance with an agreement between several states.
- Linking the value to fiat. The rate of digital currencies (cryptocurrencies, stablecoins) depends on a number of factors. The price of CBDC is more stable even when compared to fiat-backed stablecoins.

Unlike cryptocurrency, which is an independent digital asset, CBDC is a subtype of national currency. Their differences are in the convenience of use: a money transfer can be made directly, without intermediary systems and the corresponding commission. In addition, the use of digital assets is easier to track, which is important for the financial policy of the state.
Issuance and Implementation of CBDC
The implementation of the country's CBDC takes place in several stages:
- Publication of a consultative report, public consultation, conceptualization.
- Creation of a platform to launch the CBDC currency.
- Testing on a limited number of users.
- Analyzing the results of the pilot stage and deciding on the feasibility of implementation.
- Implementation.
The introduction of CBDC digital currency implies costs on the part of the financial and business sectors: preparation of equipment for payment processing, adaptation of the settlement system, and purchase of hardware are required.
In addition, it is necessary to develop protection against cyberattacks and new methods of fraud. One of the main problems is low demand: it will take a long time for the population to get used to the new payment method.

Significance and Prospects of CBDC
The request for digitalization in modern economies is due to a number of reasons:
- Stimulation of the use of national currency in settlements (relevant in countries prone to dollarization);
- stabilization of the financial sphere in the context of competition between banks and private technology and crypto companies;
- strengthening control of the financial sector, emergence of new tools to protect against fraud, misuse or illegal use of funds, etc.;
- formation of payment infrastructure with low transaction costs.
The prospects of digital currencies are influenced by a number of factors: technological, economic, social, political, ethical (in particular, the issue of confidentiality). According to experts, a complete transition to digital money in the short term is impossible. Implementation will require revision of the existing financial system, work on public awareness, and a number of legislative changes.
Nevertheless, steps in this direction are being taken in many countries around the world. Digital currency will coexist with traditional currency, gradually taking its place in the country's financial system.
CBDC: a New Form of Traditional Currencies
CBDC is a state-owned digital currency that differs from others by being centralized, controlled, and lacking anonymity. It is a modern way to strengthen a country's financial system and national currency, as well as simplify settlements and reduce their cost. Nevertheless, for many users, the lack of confidentiality is a significant disadvantage of such transactions.
Although a complete digitalization is not possible in the short term, the demand for digitalization is growing worldwide. More than 130 countries are currently developing their own digital currency.